Background
C2PA
C2PA is an open source standard that allows parties to attach metadata that is cryptographically bound to a specified image. This is done using a C2PA Manifest which is tied to a specific image, including details and metadata about said image and also a cryptographic signature over these details.
The manifest can hold any information about the photo including metadata about what device it was taken on, size of the image etc. The key point is that it is signed using some key that attests to the accuracy of the associated information.
The manifest is then embedded directly into the photo file. The manner in which this is done depends. For example, it can be embedded into the metadata section of the JPEG file, or can be embedded as an invisible watermark encoding the manifest data.
ZCAM leverages the C2PA standard to embed a verifiable zero knowledge proof that the photo was taken on an iPhone and signed using a secure enclave private key that only the ZCAM SDK can use.
Apple App Attest
ZCAM uses Apple's App Attest service to ensure that a ZPhoto was indeed signed by the ZCAM SDK.
The intended purpose of App Attest is to ensure requests coming from an app to a backend service is actually from the intended app. i.e. It guarantees that a backend service knows that it's only servicing requests from the associated mobile app.
At a high level, this is done by generating a new signing keypair on the device's secure enclave that only the specific mobile app can access. There is then a protocol for Apple to attest to the keypair as having been generated on said mobile app. This ensures any subsequent signatures using the keypair is guaranteed to be from the app.
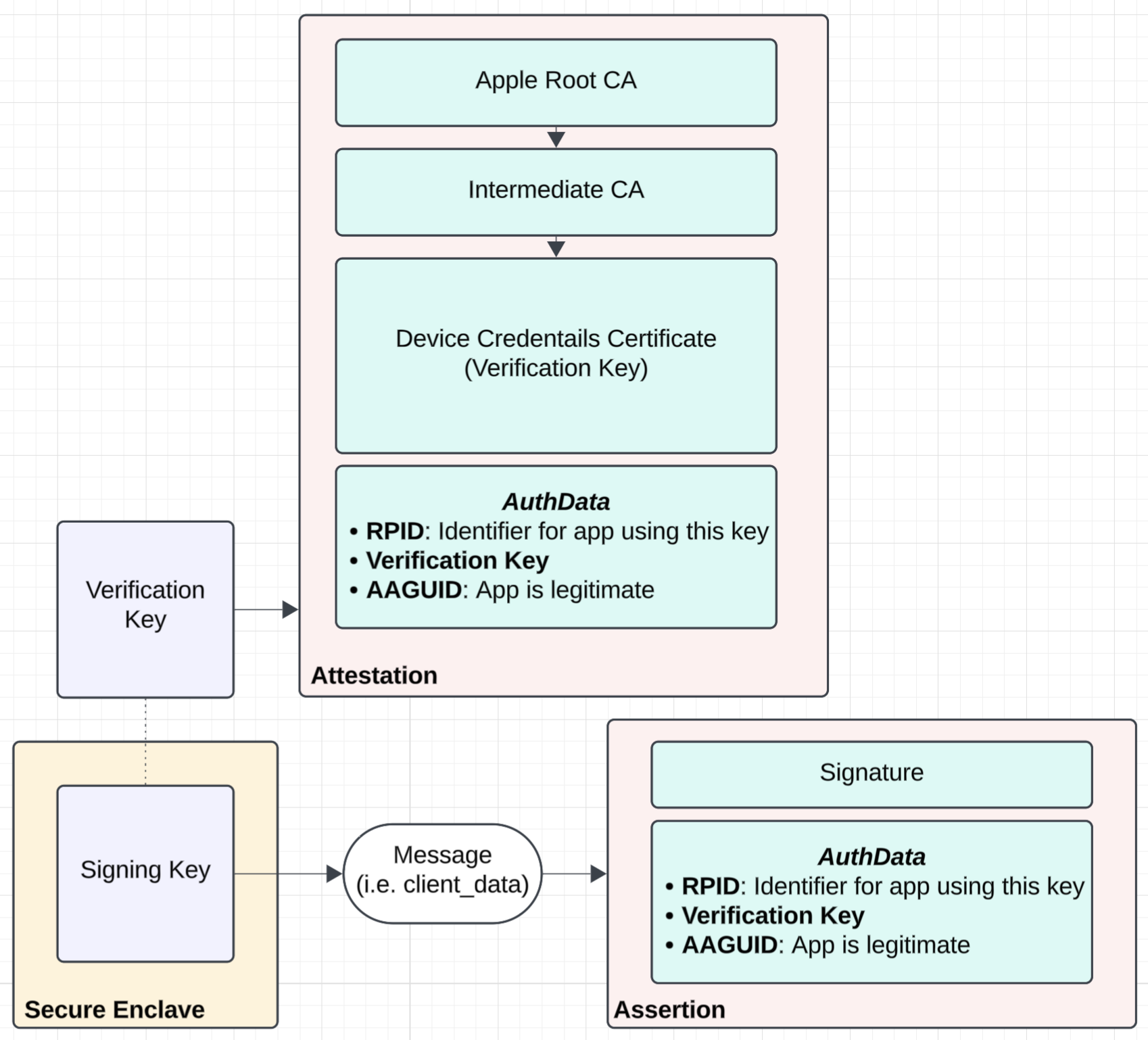
Specifically, the App Attest protocol provides an attestation from Apple's backend server that is bound to some unique nonce and the public key of the secure enclave keypair. The app can then send this attestation as part of a request, such that the receiving backend service can verify the attestation.
Note, ZCAM leverages Apple App Attest, but uses it in a subtle but different way. There are two key differences:
- The unique nonce used in the attestation is actually derived on the app itself, instead of receiving it from some backend service.
- The attestation is verified in a zero knowledge proof instead of by a backend service.
iOS Secure Enclave
TODO